Dyno2 software is equipped with powerful project and runs database that can contain lots of information about your projects. Project can be activated, for creating new runs, with double click. New projects can be created from right click menu on project list.
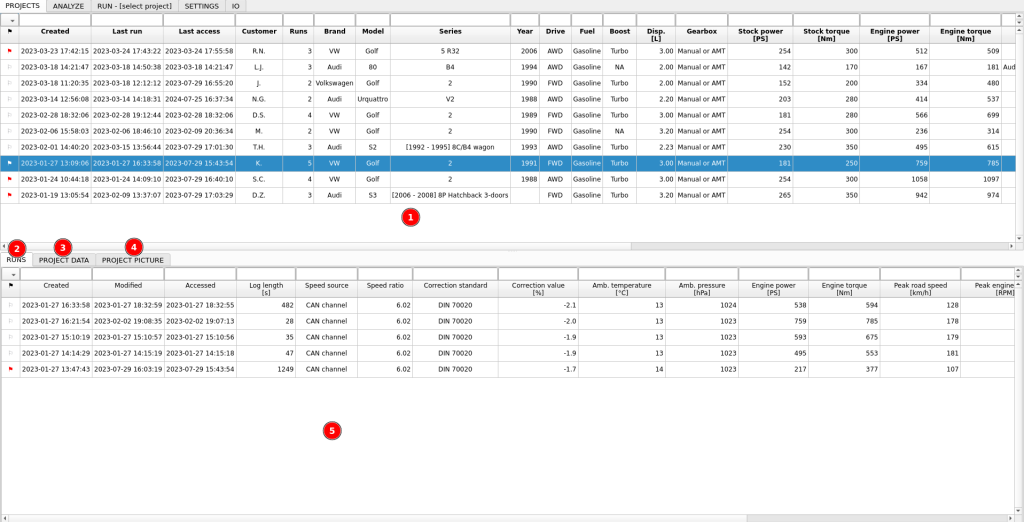
- Project list
- Tab containing runs assigned to selected project
- Tab with project configuration data
- Tab with project picture
- List of runs in selected project (when RUNS tab is selected)
Regarding the projects, two terms are used: selection and activation.
A project is selected with a single click in the project list. Tabs in the lower part of the window show runs assigned to the selected project and configuration details of the selected project.
A project is activated with a double click in the project list. New runs that you make in the RUN tab are assigned to the active project.
Information visible in project table and PROJECT DATA tab can be customized. Visibility in table end editor can be toggled. You can enter a default value for new project and select your preferred unit. The decimal field defines how many decimal places for the value will be displayed. Negative decimals value will activate scientific notation.
Project fields that have special importance
Lots of project configuration fields have only informational meaning for your reference, but there are some of these that are used for power calculation or for other software functions.
| Vehicle ID | Basic identification for project. It is shown in title bar and default report. |
| Mass Frontal Area Cx drag coefficient | Used for road simulation test. |
| Mass Drive | Used for slip estimation |
| Fuel Boost Engine efficiency Engine correction factor | Used for engine power correction calculation based on ambient conditions. |
| Vehicle type Fuel type Displacement Cylinder count Engine cycle | Used for engine inertia estimation |
| Engine inertia | Inertia connected with engine rotating parts. It can be estimated by right-clicking the field. |
| DT inertia | Inertia connected with drivetrain rotating parts – mainly wheels. It can be estimated by right-clicking from wheels size. |
| Gearbox type | Used to estimate DT loss factor |
| DT loss factor | Percent of engine power that is lost due to gearbox efficiency. Suggested values: Manual gearbox: 3-8% Hydrokinetic torque converter: 10-20% Mechanical CVT gearbox: 7-13% |
Run data recalculation
Every project contains its own runs. Runs can be analyzed with double click. Clicked runs appear in ANALYZE tab.
Runs are saved in files in /home/pi/.dyno2/runs directory. The run file contains all information required to open it on another device. The database contains only metadata required to organize your projects and runs.
A log file from a run contains raw sensor data. This way, after the run is made, if some project information was entered incorrectly, it can be adjusted and power graphs can be recalculated. The general concept is that the configuration from the SETTINGS tab is saved and fixed with the run. If something was wrong there, a new run must be made.
On the other hand changing project settings from the PROJECT tab updates the run. When you change some setting in the PROJECT DATA, the calculation is updated for all the runs currently loaded in ANALYZE tab. For performance reasons, not loaded runs from this project will be recalculated the next time they are loaded to ANALYZE tab.
You may notice that when you load the run to ANALYZE, the run stats (power, torque, etc.) in the database change. There are few possible reasons for that:
- Initially the database gets stats information from real-time data from the RUN tab. Loading a fresh run to the ANALYZE tab for the first time does a full recalculation and filtering of the data to get the most accurate result. The coastdown losses are also added to the engine power and torque at this time.
- Since only the runs loaded to the ANALYZE tab are recalculated instantly, it’s possible that the update is a result of previous changes that were made when the run was not loaded to ANALYZE tab. Some examples of these changes are:
- Changed correction standard
- Change in additional channel filtering / smoothing (Filter in Channel Setup). A filter can easily smooth down and reduce a value of a sharp peak in power.
- Change in project settings
Projects and runs data customization
Information visible for every run can be customized in similar way as for projects.